The effect of separated peptides on breast cancer (MCF-7), lung cancer (A549), and stomach cancer (AGS) cell viability was measured by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Peptide DFHINQ slightly reduced the cell viability of MCF-7 cell lines (Fig. 1). However, peptide DFHINQ seemed to act as a nutrient to AGS cell, increasing its viability (Fig. 2). This peptide had no cytotoxic effect on A549 cells (Fig. 3). 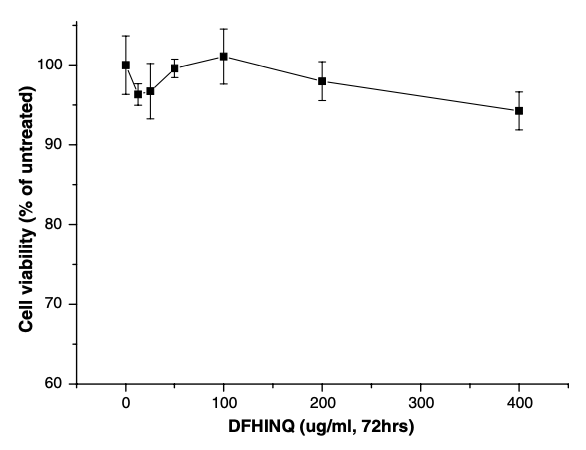 | 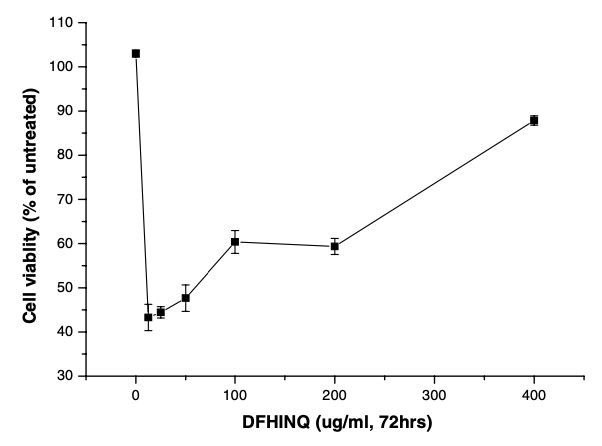 | 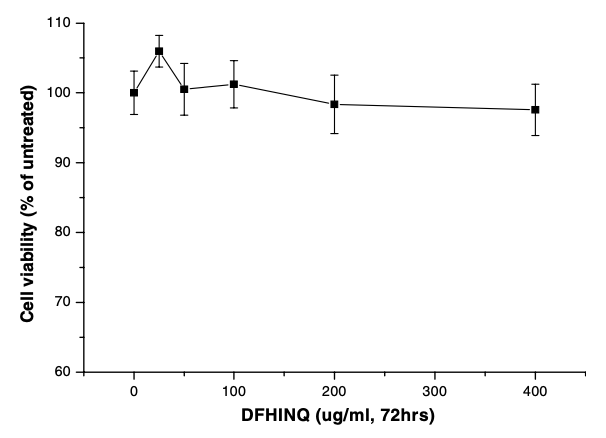 | Fig. 1. Effect of the synthetic peptide DFHINQ on cell viability of breast cancer cell line (MCF-7).
| Fig. 2. Effect of the synthetic peptide DFHINQ on cell viability of stomach cancer cell line (AGS). | Fig. 3. Effect of the synthetic peptide DFHINQ on cell viability of human lung cancer cell line (A549). |
|