Fig. 1 shows the effects of αs2-casein (164-179), αs2-casein (183-206) and αs2-casein (183-207) on Calmodulin-induced activation of 3',5'-cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE, EC 3.1.4.17). The approximate IC50 values of these peptides were 38, 6.9 and 1.1 μM respectively. The concentration of each peptide that totally inhibited the activation of PDE induced by Calmodulin had no significant effect on the basal PDE activity.
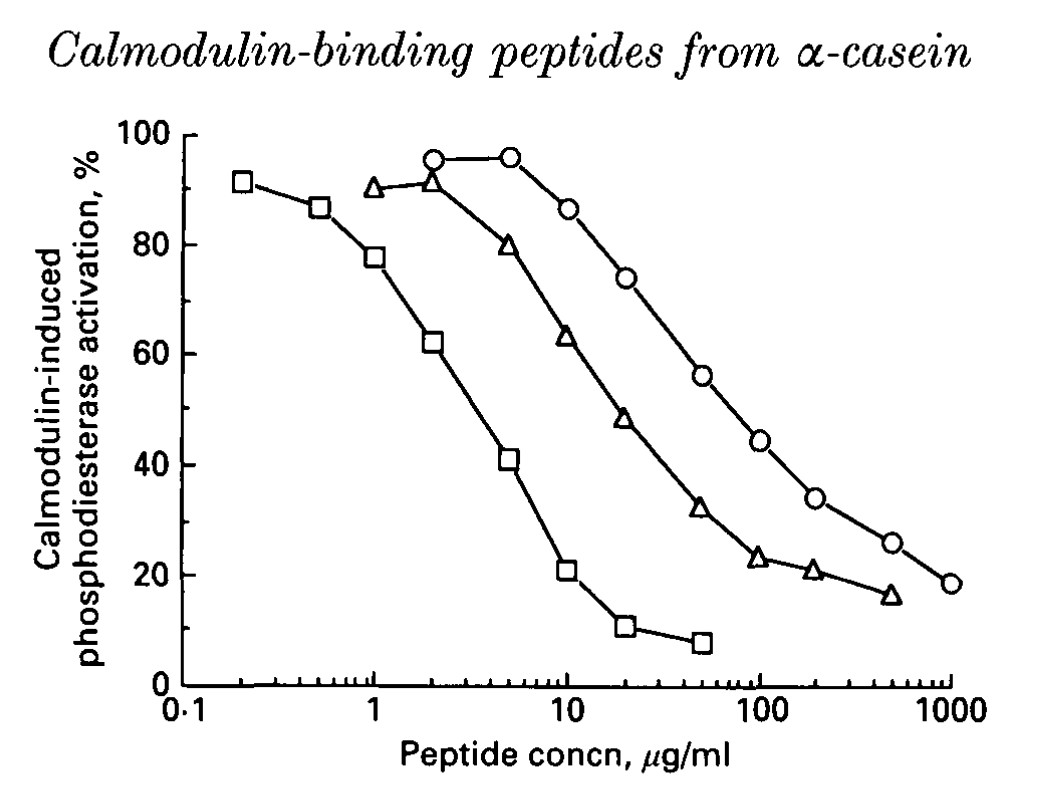 | Fig. 1. Effects of the peptides derived from α-casein on the calmodulin-indueed phosphodiesterase activation. Effects of various concentrations of ○, αs2-casein (164-179); △, αs2-casein (183-206) and □, αs2-casein (183-207) are shown. Each point is the mean of duplicate determinations.
|
|